Kanishka III
| Samrat Kanishka III | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kushan emperor | |||||
 Coin of Samrat Kanishka III. Circa AD 267–270. Main mint in Taxila. Obverse: King Kanishka standing holding a standard, sacrificing over an altar; trident to left. Greco-Bactrian legend around ϷΑΟΝΑΝΟϷΑΟ ΚΑΝΗϷΚΙ ΚΟϷΑΝΟ Shaonanoshao Kanishki Koshano "King of Kings, Kanishka the Kushan".  ga in Brahmi to right of altar; gho in Brahmi between legs; ga in Brahmi to right of altar; gho in Brahmi between legs; 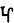 hu in Brahmi to right of scepter. Reverse: Ithyphallic Oesho (Οηϸο), thought to be Shiva, standing facing, holding a garland or diadem and trident; behind, the bull Nandi standing left; to upper left, pellet above tamgha.[1] hu in Brahmi to right of scepter. Reverse: Ithyphallic Oesho (Οηϸο), thought to be Shiva, standing facing, holding a garland or diadem and trident; behind, the bull Nandi standing left; to upper left, pellet above tamgha.[1] | |||||
| Reign | c. 265 – 275 CE | ||||
| Coronation | 265 CE | ||||
| Predecessor | Vāsishka | ||||
| Successor | Vasudeva II | ||||
| Born | 214 CE | ||||
| Died | 278 CE | ||||
| Spouse | UNKNOWN | ||||
| Issue | Shaka | ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Kushan | ||||

Samrat Kanishka III (Greco-Bactrian: ΚΑΝΗϷΚΕ Kanēške; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 Ka-ṇi-ṣka, Kaṇiṣka; Brahmi: 
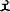
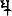 Kā-ṇi-ṣka, Kāṇiṣka; Sanskrit: कनिष्क), was a Kushan emperor who reigned from around the year 265 CE to 270 CE. He is believed to have succeeded Vasishka and was succeeded by Vasudeva II. He ruled in areas of Northwestern India.[2]
Kā-ṇi-ṣka, Kāṇiṣka; Sanskrit: कनिष्क), was a Kushan emperor who reigned from around the year 265 CE to 270 CE. He is believed to have succeeded Vasishka and was succeeded by Vasudeva II. He ruled in areas of Northwestern India.[2]
Inscriptions
In an inscription dated to the "Year 41" (probably of the 2nd century of the Kanishka era) and discovered on the borders of the river Ara in Punjab, he qualifies himself as a Maharaja rajadhiraja Devaputra Kaisara Kanishka ("Great King, King of Kings, Son of God, Caesar, Kanishka), suggesting some awareness of the Roman Empire as Kaisara seems to stand for "Caesar", and names himself as the son of Vajheshka, identified as Kushan ruler Vashishka.[3][4][5] The inscription is rather worn and the reading Kaisara has been doubted, especially since no other mentions of this title are known from Kushan sources.[6]



| Kushan emperors 30 CE–350 CE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Coinage
It was initially thought that there were no definite coins known of him, as the "Kanishka" named in the coins was not differentiated. Only workmanship and graphical style in relation to other known rulers, tend to suggest attribution to this later Kanishka.[9] However, this hypothesis was shaken by coin hoards being found in Tajikistan where coins of Kanishka III were found and identified in large numbers. All these finds north of the Oxus river seems to indicate that it was legal tender for a period of time.[10]
Notes
- ^ CNG Coins
- ^ Frye, Richard Nelson (1984). The History of Ancient Iran. C.H.Beck. p. 344. ISBN 9783406093975.
- ^ Mario Busssagli, "L'Art du Gandhara", p229
- ^ A Comprehensive History Of Ancient India (3 Vol. Set). Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. 2003. p. 134. ISBN 9788120725034.
- ^ Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017). "From the Kushans to the Western Turks". King of the Seven Climes: 203.
- ^ Rosenfield, John M. (1967). The Dynastic Arts of the Kushans. University of California Press. p. 58.
- ^ Konow, Sten (1929). Kharoshthi Inscriptions With The Exception Of Those Of Asoka. p. 163.
- ^ Konow, Sten (1929). Kharoshthi Inscriptions With The Exception Of Those Of Asoka. p. 163.
- ^ Rosenfield, John M. (1967). The Dynastic Arts of the Kushans. University of California Press.
- ^ Frye, Richard Nelson (1984). The history of ancient Iran. Munich, Germany: C.H. Beck. p. 344. ISBN 978-3-406-09397-5.
| Preceded by | Kushan Ruler | Succeeded by |













