Tétrafluorure d'hafnium
| Fluorure de hafnium(IV) | |
 | |
| Fluorure de hafnium(IV) | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | Fluorure de hafnium(IV) Tétrafluorure de hafnium |
| No CAS | 13709-52-9 |
| No ECHA | 100.033.856 |
| No CE | 237-258-0 |
| PubChem | 50925283 |
| SMILES | [F-].[F-].[F-].[F-].[Hf+4] PubChem, vue 3D |
| InChI | Std. InChI : vue 3D InChI=1S/4FH.Hf/h4*1H;/q;;;;+4/p-4 Std. InChIKey : QHEDSQMUHIMDOL-UHFFFAOYSA-J |
| Apparence | poudre cristalline blanche |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | F4HfHfF4 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 254,48 ± 0,02 g/mol F 29,86 %, Hf 70,14 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° ébullition | 970°C (se sublime)[2] |
| Masse volumique | 7,1 g/cm3[2] |
| Point d’éclair | Ininflammable |
| Cristallographie | |
| Système cristallin | Monoclinique[3] |
| Symbole de Pearson | |
| Classe cristalline ou groupe d’espace | C2/c, No. 15 |
| Paramètres de maille | a = 1,17 nm ; b = 0,986 nm ; c = 0,764 nm |
| Composés apparentés | |
| Autres cations | Fluorure de titane(IV) Fluorure de zirconium(IV) |
| Autres anions | Chlorure d'hafnium(IV) |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
modifier  | |
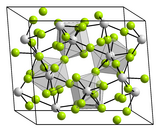
Le tétrafluorure de hafnium est un composé inorganique de formule HfF4. C'est un solide blanc. Il possède la même structure que le tétrafluorure de zirconium, avec des centres Hf(IV) en coordination 8.
Le tétrafluorure de hafnium forme un trihydrate, qui a une structure polymérique constituée d'un centre octaédrique Hf, décrit par (μ\sF)2[HfF2(H2O)2]n(H2O)n et une eau de cristallisation. Il s'agit d'un des rares cas où les chimies de Hf et de Zr diffèrent, le trihydrate de fluorure de zirconium(IV) a la structure moléculaire (μ\sF)2[ZrF3(H2O)3]2, sans l'eau de réseau[4].
Références
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ a et b (en) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, , 92nd éd., {{{pages}}} (ISBN 1439855110), p. 4.66.
- ↑ (en) W. H. Zachariasen, « Crystal chemical studies of the 5f-series of elements. XII. New compounds representing known structure types », Acta Crystallographica, vol. 2, no 6, , p. 388–390 (DOI 10.1107/S0365110X49001016
 )
) - ↑ (en) Norman N. Greenwood et Alan Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, Butterworth-Heinemann (en), , 2e éd. (ISBN 0080379419), p. 965
Voir aussi
Bibliographie
- Benjamin, S. L., Levason, W., Pugh, D., Reid, G., Zhang, W., "Preparation and structures of coordination complexes of the very hard Lewis acids ZrF4 and HfF4", Dalton Transactions 2012, 41, 12548. DOI 10.1039/C2DT31501G
v · m | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hf(II) |
| ||
| Hf(III) |
| ||
| Hf(IV) |
| ||
v · m | |
|---|---|
| Fluorures F(-I) |
|
| Interhalogènes |
|
| Tétrafluoroborates |
|
| Composés AlF6, AsF6, SbF6... |
|
| Composés NbF7, TaF7 |
|
| Perfluorocarbures |
|
| Hydrocarbures halogénés |
|
| Bifluorures |
|
| Oxohalogénures |
|
 Portail de la chimie
Portail de la chimie













